第1章 概述
1.1 目标
Nginx(发音同engine x)是一款轻量级的Web服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,由俄罗斯的程序设计师Igor Sysoev所开发,可以稳定地运行在Linux、Windows等操作系统上,其特点是占用内存少,并发能力强。
同其他软件一样,Nginx也出现过一些安全漏洞,利用这些漏洞可以对Web服务器进行渗透攻击。本文主要描述互联网架构中常用产品Nginx 的配置和安全加固工作,最终用以指导系统实施。
1.2 预期读者
本文档用于指导系统工程师进行系统实施工作,架构师和系统工程师应该通读本文档,选择适当方式用于自己的系统。
第2章 产品介绍
Nginx是一个轻量级,高性能的Web服务器/反向代理和电子邮件代理(IMAP/POP3),它可以运行在UNIX,GNU/Linux,BSD变种,MACOS X,Solaris和Microsoft Windows上。根据Netcraft的调查数据显示,互联网上11%的域名都使用了Nginx Web服务器。Nginx是解决C10K问题的服务器之一,与传统服务器不一样,Nginx不依赖于线程处理请求,相反,它使用了一个更具扩展性的事件驱动(异步)架构。Nginx在很多高流量网站上得到了应用,如WordPress,Hulu,Github和SourceForge。
第3章 Nginx的安全加固配置
3.1 Nginx版本统一
查看当前系统中部署的Nginx版本。
[root@localhostnginx]# nginx -vnginxversion: nginx/1.2.5 |
3.2 禁用autoindex
确保nginx.conf配置文件上禁用autoindex模块,即没有autoindex的配置。
加固检查:
确保nginx.conf配置文件上禁用autoindex,即autoindex off或者没有配置autoindex。
3.3 关闭服务器标记
如果开启的话(默认情况下)所有的错误页面都会显示服务器的版本和信息。nginx.conf配置如下:
http{ include naxsi_core.rules; include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; server_tokens off; ... ... |
加固检查:
[root@localhost~]# curl -I http://localhost/wavsepHTTP/1.1301 Moved PermanentlyServer:nginxDate:Tue, 31 Dec 2013 23:20:29 GMTContent-Type:text/htmlContent-Length:178Location:http://localhost/wavsep/Connection:keep-aliveKeep-Alive:timeout=30 |
其中,http://localhost/wavsep表示一个应用URL
3.4 自定义缓存
设置自定义缓存以限制缓冲区溢出攻击。nginx.conf配置如下:
http{ ... ... server{ ... ... client_body_buffer_size 16K; client_header_buffer_size 1k; client_max_body_size 1m; large_client_header_buffers 4 8k; ... ... |
注:上述的参数不是最优参数,仅供参考。
加固检查:
确保server模块中配置了上述标红的配置。
3.5 设置timeout
设置timeout设低来防御DOS攻击,nginx.conf配置如下:
http { ... ... client_body_timeout 10; client_header_timeout 30; keepalive_timeout 30 30; send_timeout 10; |
加固检查:
[root@localhost~]# curl -I http://localhost/wavsepHTTP/1.1301 Moved PermanentlyServer:nginxDate:Tue, 31 Dec 2013 23:20:29 GMTContent-Type:text/htmlContent-Length:178Location:http://localhost/wavsep/Connection:keep-aliveKeep-Alive:timeout=30 |
其中,http://localhost/wavsep表示一个应用URL
3.6 配置日志
鉴于日志的输出格式还未确定,目前暂时先使用Nginx默认的日志格式。nginx.conf配置如下:
http {
……
log_format main ‘$remote_addr – $remote_user [$time_local]”$request” ”$status $body_bytes_sent “$http_referer”””$http_user_agent” “$http_x_forwarded_for”‘;
access_log logs/ access.log main;
… …
加固检查:
查看Nginx的日志文件是否存在,并且访问应用时,有日志输出。
[root@srv-dfh526~]# tail -3f /usr/local/nginx/logs/dfh.smartcity.com.log
Client_IP:10.5.220.27 Client_IP_For:- – – [10/Jan/2014:10:42:20+0800] “method:GET /portal/images/service_6.jpg HTTP/1.1″Protocol:”http” Status:304 Size:0″http://dfh.smartcity.com/portal/ext/index/index.jsp” Args:- Browser:”Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1;Trident/5.0; BOIE9;ZHCN)”
Client_IP:10.1.108.133 Client_IP_For:- – – [10/Jan/2014:10:42:23+0800] “method:GET/search/search?collId=1,2,3,4,5,6&query=%B3%C7%CA%D0%B9%E3%B2%A5HTTP/1.1″ Protocol:”http” Status:200 Size:4145″http://dfh.smartcity.com/search/search?collId=1,2,3,4,5,6&query=%E5%9F%8E%E5%B8%82%E5%B9%BF%E6%92%AD&appID=1&ucode=utf-8″ Args:- Browser:”Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML,like Gecko) Chrome/30.0.1599.101 Safari/537.36″
Client_IP:10.5.220.27 Client_IP_For:- – – [10/Jan/2014:10:42:24+0800] “method:GET /portal/images/change/service1_1.png HTTP/1.1″Protocol:”http” Status:304 Size:0″http://dfh.smartcity.com/portal/ext/index/index.jsp” Args:- Browser:”Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1;Trident/5.0; BOIE9;ZHCN)”
注:日志输出格式需要看配置的情况。
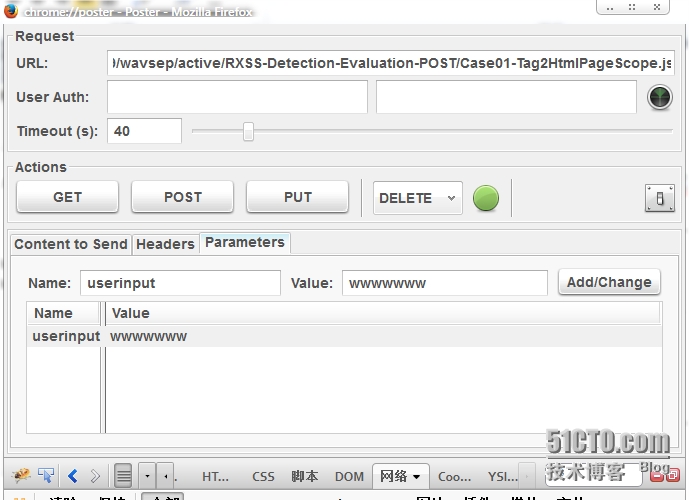
3.7 限制访问的方法
在目前的应用系统中值使用到POST和GET方法,所以除了它们之外,其他方式的请求均可拒绝。Nginx.conf配置如下:
server{ ... ... if($request_method !~ ^(GET|HEAD|POST)$) { return404; } ... ... |
注:因为目前统一错误应用没有定版,所以先使用404,实际中应该使用444.
加固检查:
使用火狐浏览器的poster插件:
尝试使用不同的请求方式试试,能不能访问。
3.8 Nginx日志切割
Nginx日志主要用于日后的审计和分析,对系统的安全有着重要的意义。但是随着时间的推移,日志文件会变得越来越大,这就需要对日志进行处理分割了。
第一步:建立脚本文件:
[root@localhosthome]# vim nginx_log.sh#/bin/bash |
#日志将要存放的路径
savepath_log='/logs/nginx/logs' |
#nginx的日志路径
nglogs='/usr/logs' mkdir-p $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date +%m)mv$nglogs/centoshost.com.log $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date+%m)/centoshost$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M).logmv$nglogs/wavsep.com.log $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date +%m)/wavsep$(date+%Y%m%d%H%M).logkill-USR1 $(cat /var/run/nginx/nginx.pid) |
其中,savepath_log和nglogs分别表示日志分割后的存放目录和Nginx的日志目录,均需要根据实际情况修改;centoshost.com.log和wavsep.com.log为Nginx现在的文件文件名称,也需要根据实际情况修改;centoshost和wavsep表示切割后保存的日志文件名称,需要根据实际情况修改。
第二步:为nginx_log.sh分配可以执行权限
[root@localhost home]# chmod 755 nginx_log.sh
第三步:设定定时器
[root@localhostinit.d]# crontab -e0000 * * * /home/nginx_log.sh #执行文件存放路径,每天凌晨00:00执行 |
注:保存方式与vim一致,输入:wq。
第四部:重启定时器
[root@localhostinit.d]# cd /etc/init.d[root@localhostinit.d]# ./crond restart停止 crond: [确定]正在启动 crond: [确定] |
过程图:
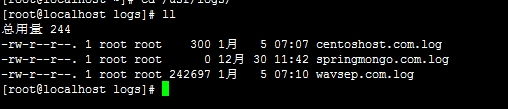
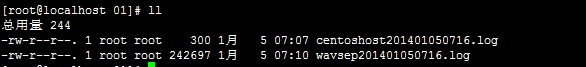
第一:Nginx日志切割前
第二:保存日志的目录(切割前)
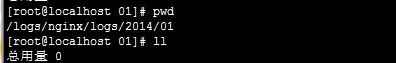
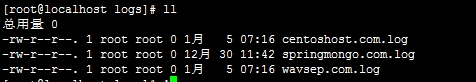
第三:Nginx日志切割后
第四:保存日志的目录(切割后)
3.9 限制访问IP
模块 ngx_http_access_module 允许限制某些IP地址的客户端访问。
如下范例:
location/ {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
allow 2001:0db8::/32;
deny all;
}
注:规则按照顺序依次检测,直到匹配到第一条规则。 在这个例子里,IPv4的网络中只有 10.1.1.0/16 和 192.168.1.0/24允许访问,但 192.168.1.1除外, 对于IPv6的网络,只有2001:0db8::/32允许访问。
3.10集成Naxsi模块
Naxsi模块的集成,是基于Nginx已经部署了或已经存在系统中。
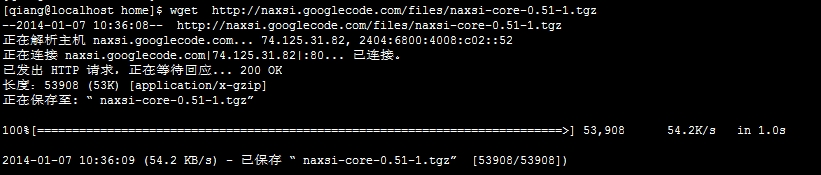
第一步:下载naxsi
[qiang@localhosthome]$ wget http://naxsi.googlecode.com/files/naxsi-core-0.51-1.tgz
注:如果不能上网可以事先下载,再上传到服务器中。
第二步:解压naxsi
[qiang@localhost install]$ tar -zxvfnaxsi-core-0.51-1.tgz
第三步:切换到naxsi-core-0.51-1目录,并复制其配置文件到nginx.conf同目录下
[qiang@localhostnaxsi_config]$ cp naxsi_core.rules /etc/nginx/naxsi_core.rules
修改naxsi_core.rules的配置如下:
##################################
## INTERNAL RULESIDS:1-999 ##
##################################
#@MainRule “msg:weirdrequest, unable to parse” id:1;
#@MainRule”msg:request too big, stored on disk and not parsed” id:2;
#@MainRule”msg:invalid hex encoding, null bytes” id:10;
#@MainRule”msg:unknown content-type” id:11;
#@MainRule”msg:invalid formatted url” id:12;
#@MainRule “msg:invalidPOST format” id:13;
#@MainRule”msg:invalid POST boundary” id:14;
##################################
## SQL InjectionsIDs:1000-1099 ##
##################################
MainRule”rx:select|union|update|delete|insert|table|from|ascii|hex|unhex|drop””msg:sql keywords” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$SQL:8″ id:1000;
MainRule”str:\”” “msg:double quote””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:8,$XSS:8″id:1001;
MainRule”str:0x” “msg:0x, possible hex encoding””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:2″ id:1002;
## Hardcore rules
MainRule”str:/*” “msg:mysql comment (/*)””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:8″ id:1003;
MainRule”str:*/” “msg:mysql comment (*/)””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:8” id:1004;
MainRule “str:|””msg:mysql keyword (|)” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:8″id:1005;
##MainRule”str:&&” “msg:mysql keyword (&&)””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:8″ id:1006;
## end of hardcore rules
MainRule”str:–” “msg:mysql comment (–)””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:4” id:1007;
MainRule “str:;””msg:; in stuff” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS””s:$SQL:4,$XSS:8” id:1008;
MainRule “str:=””msg:equal in var, probable sql/xss” “mz:ARGS|BODY””s:$SQL:2” id:1009;
MainRule “str:(“”msg:parenthesis, probable sql/xss””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:4,$XSS:8″id:1010;
MainRule “str:)””msg:parenthesis, probable sql/xss””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:4,$XSS:8″id:1011;
MainRule “str:'””msg:simple quote” “mz:ARGS|BODY|URL|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$SQL:4,$XSS:8” id:1013;
MainRule “str:,””msg:, in stuff” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$SQL:4” id:1015;
MainRule “str:#””msg:mysql comment (#)””mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$SQL:4″ id:1016;
###############################
## OBVIOUS RFIIDs:1100-1199 ##
###############################
MainRule”str:http://” “msg:http:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1100;
MainRule”str:https://” “msg:https:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1101;
MainRule”str:ftp://” “msg:ftp:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1102;
MainRule”str:php://” “msg:php:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1103;
MainRule”str:sftp://” “msg:sftp:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1104;
MainRule”str:zlib://” “msg:zlib:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1105;
MainRule”str:data://” “msg:data:// scheme” “mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$RFI:8″ id:1106;
MainRule”str:glob://” “msg:glob:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1107;
MainRule”str:phar://” “msg:phar:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8″ id:1108;
MainRule”str:file://” “msg:file:// scheme””mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$RFI:8” id:1109;
#######################################
## Directory traversalIDs:1200-1299 ##
#######################################
MainRule “str:..””msg:double dot” “mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$TRAVERSAL:4″ id:1200;
MainRule”str:/etc/passwd” “msg:obvious probe””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$TRAVERSAL:4″id:1202;
MainRule”str:c:\\” “msg:obvious windows path” “mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$TRAVERSAL:4″ id:1203;
MainRule”str:cmd.exe” “msg:obvious probe””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$TRAVERSAL:4″id:1204;
MainRule”str:\\” “msg:backslash””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$TRAVERSAL:4″id:1205;
MainRule “str:/””msg:slash in args” “mz:ARGS|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$TRAVERSAL:2″ id:1206;
########################################
## Cross Site ScriptingIDs:1300-1399 ##
########################################
MainRule”str:<” “msg:html open tag””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8″ id:1302;
MainRule”str:>” “msg:html close tag””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8” id:1303;
MainRule “str:[“”msg:[, possible js” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$XSS:4” id:1310;
MainRule “str:]””msg:], possible js” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$XSS:4” id:1311;
MainRule “str:~””msg:~ character” “mz:BODY|URL|ARGS|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$XSS:4″ id:1312;
MainRule”str:`” “msg:grave accent!” “mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8″id:1314;
MainRule “rx:%[2|3].” “msg:double encoding !””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8” id:1315;
MainRule “rx:%3[c|e].” “msg:double encoding !””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8” id:1316;
MainRule “rx:\\\u003[c|e]” “msg:tag encoding !””mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$XSS:8” id:1317;
MainRule “str:&#” “msg:utf7/8 encoding” “mz:ARGS|URL|BODY|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie””s:$EVADE:4” id:1318;
####################################
## Evading tricks IDs:1400-1500 ##
####################################
MainRule”str:&#” “msg: utf7/8 encoding””mz:ARGS|BODY|URL|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$EVADE:4″id:1400;
MainRule”str:%U” “msg: M$ encoding””mz:ARGS|BODY|URL|$HEADERS_VAR:Cookie” “s:$EVADE:4″id:1401;
MainRule negative”rx:multipart/form-data|application/x-www-form-urlencoded””msg:Content is neither mulipart/x-www-form..””mz:$HEADERS_VAR:Content-type” “s:$EVADE:4″ id:1402;
#############################
## File uploads: 1500-1600##
#############################
MainRule”rx:.ph|.asp|.ht” “msg:asp/php file upload!””mz:FILE_EXT” “s:$UPLOAD:8” id:1500;
MainRule “rx:.jsp””msg:asp/php file upload!” “mz:FILE_EXT””s:$UPLOAD:8” id:1501;
MainRule “rx:.html””msg:asp/php file upload!” “mz:FILE_EXT””s:$UPLOAD:8” id:1502;
MainRule “rx:.php””msg:asp/php file upload!” “mz:FILE_EXT””s:$UPLOAD:8” id:1503;注:(1)nginx.conf所有的目录是在nginx编译安装时,默认的配置是<prefix>/conf/nginx.conf。
(2)鉴于原有的naxsi_core.rules文件中规则不足,最好是采用本文档中的配置规则。
第四步:编译安装Nginx
查看系统原来编译Nginx的参数:
[qiang @srv-dfh526 ~]#nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.3.0
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments:–with-http_stub_status_module –with-http_gzip_static_module–with-http_ssl_module –prefix=/usr/local/nginx–with-openssl=/root/install/openssl-1.0.1c –with-pcre=/root/install/pcre-8.20
在原来的编译参数的首行加入–add-module=/root/install/naxsi-core-0.51-1/naxsi_src。
[qiang@localhostnginx-1.5.7]#./configure
–add-module=/root/install/naxsi-core-0.51-1/naxsi_src\
–with-http_stub_status_module\
–with-http_gzip_static_module\
–with-http_ssl_module \
–prefix=/usr/local/nginx\
–with-openssl=/root/install/openssl-1.0.1c\
–with-pcre=/root/install/pcre-8.20
[root@localhostnginx-1.5.7]# make && make install
注:上述的参数可以根据实际情况选择,但是标红的需要有。
第五步:验证nginx是否安装成功
[qiang@localhostnginx-1.5.7]# nginx
nginx: [warn] low addressbits of 192.168.1.65/26 are meaningless in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:78
[qiang@localhostnginx-1.5.7]# ps -ef |grep nginx
root 3086 1 0 10:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx
root 3087 3086 1 10:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3088 3086 1 10:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3089 3086 1 10:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3090 3086 1 10:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3093 3073 4 10:53 pts/1 00:00:00 grep nginx
第六步:配置过滤条件
切换目录到与nginx.conf同目录下,新建nbs.rules文件。
[qiang@localhost nginx]#vim nbs.rules
##LearningMode;
#Enables learningmode–stop
SecRulesEnabled;
##Disables learning
##SecRulesDisabled;
DeniedUrl”/RequestDenied”;
## check rules
CheckRule “$SQL >=8” BLOCK;
CheckRule “$RFI >=8” BLOCK;
CheckRule “$TRAVERSAL>= 8” BLOCK;
CheckRule “$EVADE>= 8” BLOCK;
CheckRule “$XSS >=8” BLOCK;
###########################################################
## STOP ALL RULES(如果不需要可以关闭全部过滤规则) ##
############################################################
#BasicRule wl:0;
##################################
## INTERNAL RULESIDS:1-999 ##
##################################
BasicRulewl:1,2,10,11,12,13,14;
##################################
## SQL InjectionsIDs:1000-1099 ##
##################################
BasicRule wl: 1000,1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1011,1012,1013,1014,1015,1016;
###############################
## OBVIOUS RFIIDs:1100-1199 ##
###############################
BasicRulewl:1100,1101,1102,1103,1104,1105,1106,1107,1108,1109;
#######################################
## Directory traversalIDs:1200-1299 ##
#######################################
BasicRulewl:1200,1202,1203,1204,1205,1206;
########################################
## Cross Site ScriptingIDs:1300-1399 ##
########################################
BasicRulewl:1310,1311,1312,1313,1314,1315,1318;
####################################
## Evading tricks IDs:1400-1500 ##
####################################
BasicRulewl:1400,1401,1402;
#############################
## File uploads: 1500-1600##
#############################
BasicRule wl:1500,1501,1502,1503;
注:该nbs.rules文件的规则需要根据不同的业务应用制定。
第七步:配置nginx.conf
http{
#必须配置
include naxsi_core.rules;
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
…….
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost centoshost.com;
charset utf-8;
…….
location /wavsep/ {
…….
#每一个location配置首行都需要添加该行
includenbs.rules;
…….
}
#与应用处于相同的server配置
location /RequestDenied {
error_page 404 /404.html;
}
注:wavsep表示一个demo应用。
第八步:重启nginx
[qiang@localhostnginx]# nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx:[warn] low address bits of 192.168.1.65/26 are meaningless in/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:78
nginx:the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx:configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[qiang@localhostnginx]# nginx -s reload
nginx:[warn] low address bits of 192.168.1.65/26 are meaningless in/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:78
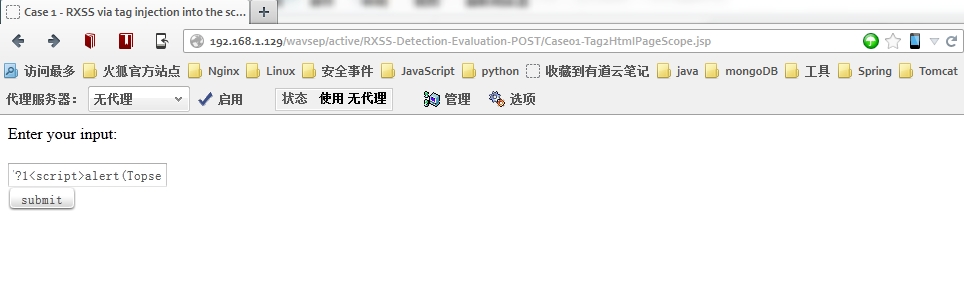
第九步:测试拦截规则是否启用
上述的规则仅过滤“<”、“>”。
测试XSS注入:
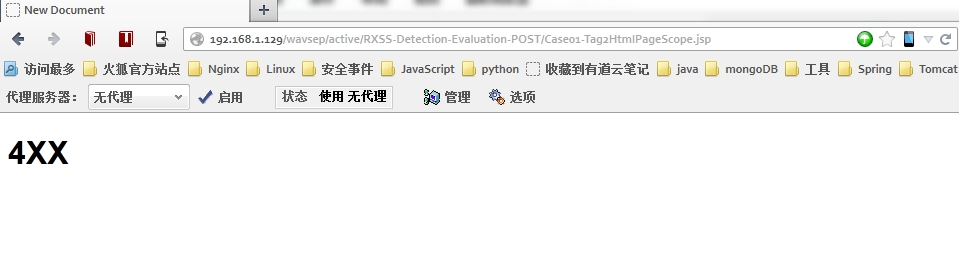
结果:
第十步:替换应用中的ajax
function htmlEncode (str){ var s = ""; if (str.length == 0) return ""; //s = str.replace(/ /g, " "); //s = str.replace(/&/g, "&"); s = str.replace(/</g, "<"); s=s.replace(/%3C/g,"<"); s=s.replace(/%3c/g,"<"); s = s.replace(/>/g, ">"); s = s.replace(/%3E/g, ">"); s = s.replace(/%3e/g, ">"); //s = s.replace(/\'/g, "'"); //s = s.replace(/\"/g, """); //s = s.replace(/\n/g, "<br>"); return s;}function ajaxJsonCall(url, data, callback) { var source=""; if(typeof(data) == "object"){ source=htmlEncode(JSON.stringify(data)); source=JSON.parse(source); data=source; }else if(typeof(data) == "string"){ source=htmlEncode(data); data=source; } $.ajax({ url: app_path + '/' + url, //contentType: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8", data: data, type: "POST", dataType: "json", error:function(msg){msg.rtnCode='999999';msg.rtnMsg='发生未知异常';callback(msg)}, success: callback }); /*data = replacechar(data); $.post(app_path + '/' + url, data, callback, 'json');*/} |